|
Program financed by: Ministry of Research and Innovation, CNCS – UEFISCDI, within PNCDI III
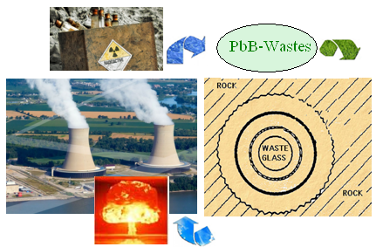
Summary of the project: Borosilicate and phosphate glasses were tested and used to immobilize radioactive wastes generated from reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel. Borosilicate glasses were chosen as the first generation preferred host matrix due to their high chemical durability and good thermal stability. Synthesis of borosilicate glasses by melt quenching method requires relatively high process temperatures (1200 - 1500 °C) for effective encapsulation of waste. This high temperature is a major drawback because of certain isotopes and heavy metals can occur, requiring the use of secondary treatment systems to capture and stabilize these of gas contaminants. The phosphate glass systems have a low melting point but have little commercial applicability due to their rapid degradation in water and poor chemical durability. On the other hand, the impossibility of use of radioactive elements defines certain limitations of current approaches. Hence, it is quite essential to search alternative host matrices to immobilize these problematic radioactive wastes. The final goal of the proposed project is: i) to study of enhanced immobilization capacities, improved durability and superior irradiation stability in a series of simulated lead-borate glasses with rare earth ions synthesized at lower manufacturing temperature by an easier processing route - melt quenching method. Sm and Tb ions are used in order to “simulate” the behavior of uranium or plutonium ions that represents an important segment of the radioactive waste. ii) to elaborate a theoretic model for simulated waste immobilization in glasses. In brief, if the issues mentioned above concerning the important proposed research topic will be understood and controlled, new opportunities and solutions for integrated radioactive wastes management will be opened.
|

|
Project Leader: Sen. Res. Sc. III. Dr. DEHELEAN Augusta-Adriana National Institute for Research and Development of Isotopic and Molecular Technologies
Mentor: Sen. Res. Sc. I. Habil. Dr. RADA Simona National Institute for Research and Development of Isotopic and Molecular Technologies E-mail address: simona.rada@itim-cj.ro Copyright © INCDTIM 2018 All rights reserved
|
|
Lead-borate glasses and vitroceramics containing simulated radioactive wastes |