Dissemination to the public
Presentation of the results for the dissemination of the Contracting Authority
Water is the source of life and an essential resource for human survival. With fast socio-economic development and increasing population worldwide, the water environment crisis has drawn widespread concern for humanity nowadays. An improvement of water supply and sanitation, and better management of water resources, especially in terms of water reuse, can significantly contribute to poverty reduction and boost economic growth in low-income countries. Responding to these requirements, adopting new ecologically and environmentally friendly technologies is necessary.
Polymer membrane filtration is considered a green technology for water treatment. One of the widely used polymers for membrane fabrication is polyvinylidene fluoride PVDF, which exhibits high mechanical strength, strong resistance to chemical and physical degradation, biological oxidation, and irradiation deterioration which are very important for the application of separation membranes. However, PVDF is hydrophobic, which increases the susceptibility of PVDF-based membranes for fouling. High hydrophobicity not only requires higher membrane pressure during usage, but also hydrophobic pollutants adsorbed on the membrane surface or inside the membrane pores lead to severe membrane fouling. Membrane fouling can cause serious declines in water flux and shorten membrane life. Therefore, it is imperative to increase the hydrophilicity of PVDF membranes by preparing low-pollution or non-pollution PVDF membranes. In this project were combined three components with complementary functionalities: ZnO-MFe2O4 (M = Zn, Co, Ni) nanocomposite heterostructure with PVDF to obtain ultrafiltration membrane with photocatalytic activity under visible irradiation.
More precisely, optimized photoactive heterostructures of the MFe2O4-ZnO type were obtained, and using magnetic field were manipulated assuring a good distribution on the surface and in the pores of the PVDF membranes, giving them a better hydrophilicity and self-cleaning properties under the action of visible light.
A scheme of our approach is shown below.
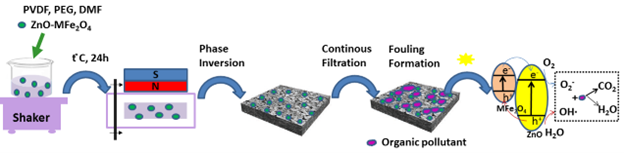
The obtained results generated the following effects:
- The preparation methods regarding MFe2O4-ZnO type heterostructures, (M=Zn, Co, Ni) were optimized and it was identified how their photocatalytic properties are influenced by the position of the cations in the tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the spinel ferrites, by the ratio between the heterostructures components and the intermediate layer between them.
- The preparation method of PVDF-MFe2O4-ZnO type membranes was optimized, so that the photoactive heterostructures are distributed on the surface and in the pores of the membranes under the action of the magnetic field.
- Dissemination in: 5 ISI papers (3 ISI papers published and 2 ISI papers-under evaluation), 6 Communications at International Conferences.
